A digital revolution is transforming the landscape of American businesses, with digital twin technology at the forefront of this change. Once the stuff of science fiction, digital twins are now a strategic necessity for organizations aiming to optimize operations, improve decision-making, and foster innovation.
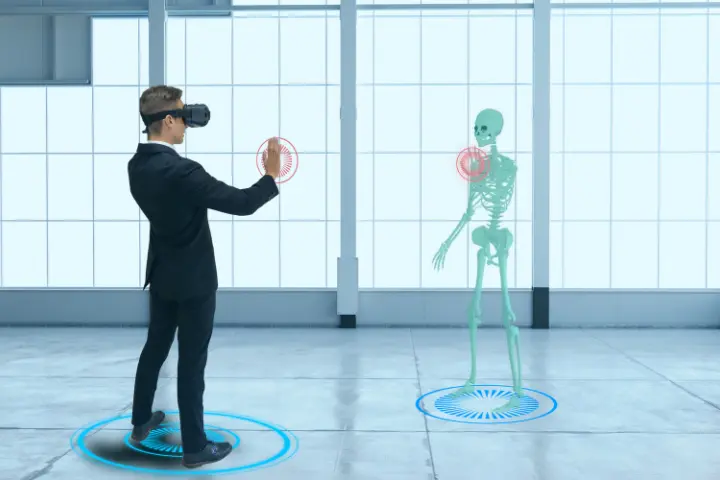
What is a Digital Twin?
A digital twin is a dynamic virtual model that mirrors the state of a physical asset or process in real time. Sensors embedded in physical objects or systems collect and transmit data, creating a comprehensive digital representation. This virtual replica empowers organizations to simulate, predict, and optimize performance, leading to operational excellence and informed decision-making.
Building a Digital Twin: A Multi-Step Process
Constructing a robust digital twin requires careful planning and the integration of several key components:
- Data Acquisition: The foundation gathers accurate, real-time data from physical assets. This involves deploying sensors, integrating various data sources, and ensuring data quality.
- Model Development: Creating a virtual representation necessitates advanced modeling techniques and domain expertise specific to the replicated asset or process.
- Simulation and Analysis: Running simulations allows organizations to predict outcomes, identify bottlenecks, and optimize performance.
- Integration and Visualization: Integrating the digital twin with existing systems and providing user-friendly visualizations are crucial for user adoption.
Real-World Applications of Digital Twins
Let’s explore specific use cases and implementation strategies for digital twins across various industries.
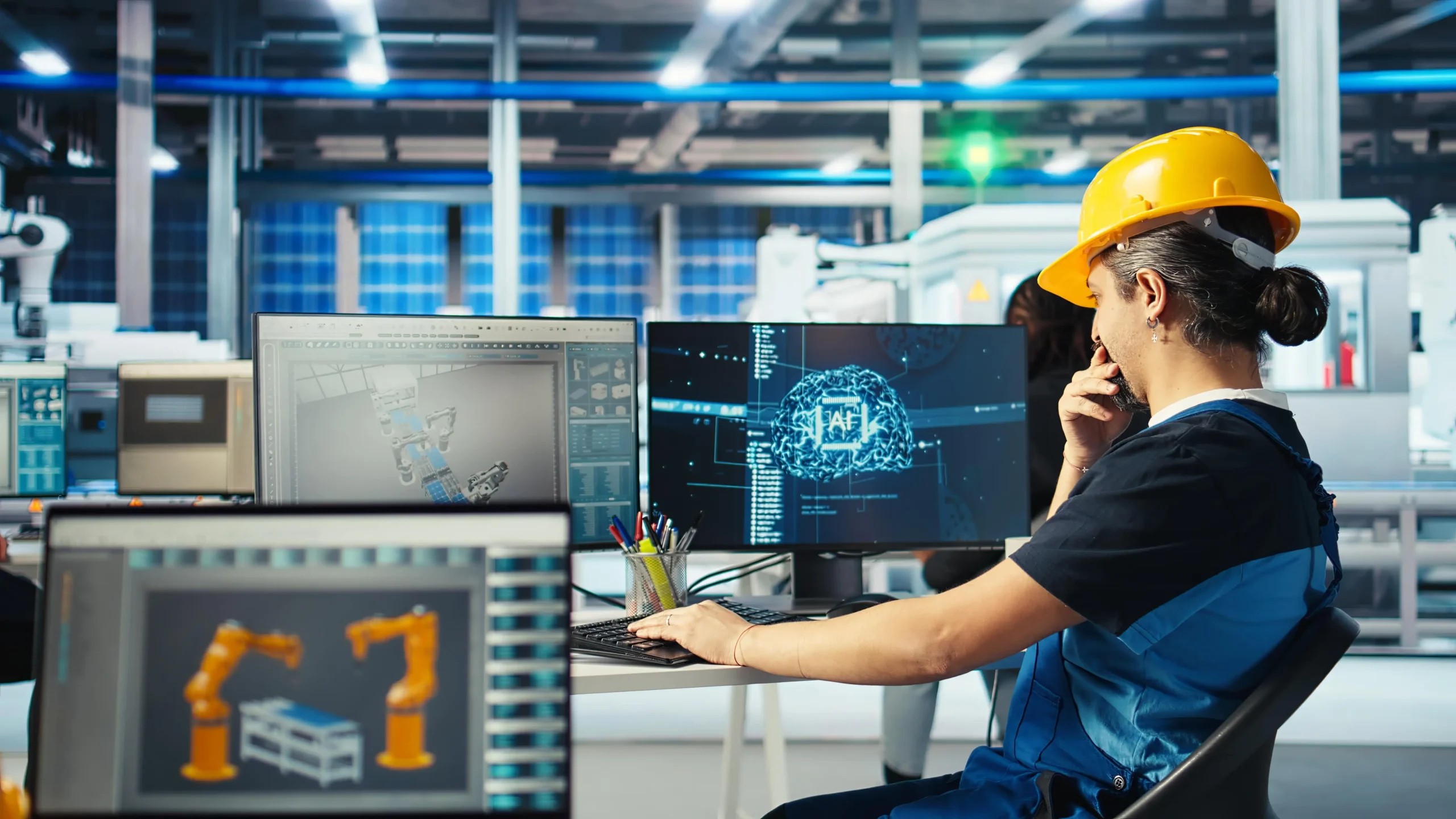
Manufacturing: Optimizing Production and Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance: By monitoring equipment performance in real-time, manufacturers can predict failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and optimizing maintenance schedules.
- Quality Control: Digital twins can simulate product assembly, identify potential defects, and improve product quality.
- Supply Chain Optimization: By creating digital twins of the entire supply chain, manufacturers can optimize logistics, reduce costs, and improve responsiveness.
Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care
- Precision Medicine: Digital twins of patients can be utilized to personalize treatment plans based on individual genetic makeup and medical history.
- Surgical Planning: Surgeons can practice complex procedures on virtual replicas of patients, reducing risks and improving outcomes.
- Drug Development: Digital twins can accelerate drug development by simulating drug interactions and predicting efficacy.
Energy and Utilities: Building a Smarter Grid
- Asset Management: Creating digital twins of power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks enables optimized maintenance and asset lifecycle management.
- Grid Optimization: Simulating different scenarios helps utilities improve grid reliability and efficiency.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Digital twins can foster the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid.
Other Industries
Digital twins have applications in various other industries, including:
- Automotive: Optimizing vehicle design, manufacturing, and maintenance.
- Aerospace: Improving aircraft design, maintenance, and flight operations.
- Retail: Enhancing customer experiences, optimizing store layouts, and managing inventory.
- Urban Planning: Simulating city infrastructure, traffic patterns, and resource allocation.
Implementing Digital Twins
Successfully implementing a digital twin requires a systematic approach:
- Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the digital twin’s goals and the value it will bring to the organization.
- Data Collection: Identify and integrate relevant data sources, ensuring data quality and security.
- Model Development: Create a detailed virtual representation of the physical asset or process.
- Simulation and Analysis: Conduct simulations to test different scenarios and identify optimization opportunities.
- Visualization: Develop user-friendly interfaces for interacting with the digital twin.
- Integration: Integrate the digital twin with existing systems and workflows.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly update and refine the digital twin based on new data and insights.
The Economic Impact of Digital Twins
According to McKinsey’s report, digital twins can create trillions of dollars in value across various industries within the US. Businesses investing in this technology can expect significant efficiency, productivity, and innovation improvements.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are substantial, implementing digital twins requires careful planning and execution. Addressing data privacy, security, and integration challenges is crucial. Developing in-house expertise in digital twin technologies is essential for successful implementation.
The Future of Digital Twins
As technology evolves, digital twins will grow increasingly sophisticated and interconnected. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoT) will further elevate their potential. By adopting digital twins, U.S. organizations can tap into new opportunities, make more informed decisions, and secure a competitive edge in the digital era.